Below are the most frequently asked SAS interview questions, along with answers. This will give you the confidence to crack your SAS interview. These questions cover a wide range of topics, from simple theoretical concepts to tricky interview questions for both freshers and experienced SAS programmers.
1. Difference between INPUT and INFILE
The INFILE statement is used to identify an external file while the INPUT statment is used to describe your variables.
FILENAME TEST 'C:\DEEP\File1.xls'; DATA READIN; INFILE TEST; LENGTH NAME $25; INPUT ID NAME$ SEX; RUN;
Note : The variable name, followed by $ (dollar sign), idenfities the variable type as character.
In the example shown above, ID and SEX are numeric variables and Name a character variable.
2. Difference between Informat and Format
Informats read the data while Formats write the data.
Informat - To tell SAS that a number should be read in a particular format. For example: the informat mmddyy6. tells SAS to read the number121713as the date December 17, 2013.
Format - To tell SAS how to print the variables.
3. Difference between Missover and Truncover
Missover -When the MISSOVER option is used on the INFILE statement, the INPUT statement does not jump to the next line when reading a short line. Instead, MISSOVER setsvariables to missing.
Truncover - It assigns the raw data value to the variable even if the value is shorter than the length that is expected by the INPUT statement.
The following is an example of an external file that contains data:
1 22 333 4444
This DATA step uses the numeric informat 4. to read a single field in each record of raw data and to assign values to the variable ID.
data readin; infile 'external-file' missover; input ID4.; run; proc print data=readin; run;The output is shown below :
Obs ID 1 . 2 . 3 . 4 4444Truncover
data readin; infile 'external-file' truncover; input ID4.; run; proc print data=readin; run;
The output is shown below :
Obs ID 1 1 2 22 3 333 4 4444
4. Purpose of double trailing@@ in Input Statement ?
The double trailing sign (@@)tells SAS rather than advancing to a new record, hold the current input record for the execution of the next INPUT statement.
DATA Readin; Input Name $ Score @@; cards; Sam 25 David 30 Ram 35 Deeps 20 Daniel 47 Pars 84 ; RUN;
The output is shown below :
 |
| Double Trailing |
5. How to include or exclude specific variables in a data set?
- DROP, KEEP Statements and Data set Options
The DROP statement specifies the names of the variables that you want to remove from the data set.
data readin1; set readin; drop score; run;
The KEEP statement specifies the names of the variables that you want to retain from the data set.
data readin1; set readin; keep var1; run;DROP, KEEP Data set Options
The main difference between DROP/ KEEP statement and DROP=/ KEEP=data set option is that you can not use DROP/KEEP statement in procedures.
data readin1 (drop=score); set readin; run; data readin1 (keep=var1); set readin; run;
6. How to print observations 5 through 10 from a data set?
The FIRSTOBS= and OBS=data set options would tell SAS to print observations 5 through 10 from the data set READIN.
proc print data = readin (firstobs=5 obs=10); run;
7.What are the default statistics that PROC MEANS produce?
PROC MEANS produce the "default" statistics of N, MIN, MAX, MEAN and STD DEV.
Proc Means : Detailed Explanation8. Name and describe functions that you have used for data cleaning?
 |
| SAS Character Functions |
9. Difference between FUNCTION and PROC
Example : MEAN function and PROC MEANS
The MEAN function is an average of the value of several variables in one observation. The average that is calculated using PROC MEANS is the sum of all of the values of a variable divided by the number of observations in the variable. In other words, the MEAN function will sum across the row and a procedure will SUM down a column.
MEAN FunctionAVG=MEAN (of Q1 - Q3);
See the output below :
 |
| MEAN Function Output |
PROC MEANS DATA=READIN MEAN; RUN;
The output is shown below :
 |
| PROC MEANS Output |
10. Differences between WHERE and IF statement?
For detailed explanation, see this tutorial -SAS : Where Vs IF
- WHERE statement can be used in procedures to subset data while IF statement cannot be used in procedures.
- WHERE can be used as a data set option while IF cannot be used as a data set option.
- WHERE statement is more efficient than IF statement. It tells SAS not to read all observations from the data set
- WHERE statement can be used to search for all similar character values that sound alike while IF statement cannot be used.
- WHERE statement can not be used when reading data using INPUT statement whereas IF statement can be used.
- Multiple IF statements can be used to execute multiple conditional statements
- When it is required to use newly created variables, useIF statement as it doesn't require variables to exist in the READIN data set
11. What is Program Data Vector (PDV)?
PDV is a logical area in the memory.How PDV is created?
SAS creates a dataset one observation at a time.Input buffer is created at the time of compilation, for holding a record from external file.PDV is created followed by the creation of input buffer.SAS builds dataset in the PDV area of memory.
Detailed Explanation : How PDV Works
12. What is DATA _NULL_?
The DATA _NULL_ is mainly used to create macro variables. It can also be used to write output without creating a dataset.The idea of "null" here is that we have a data step that actually doesn't create a data set.
13. What is the difference between '+' operator and SUM function?
SUM function returns the sum of non-missing arguments whereas “+” operator returns a missing value if any of the arguments are missing.
Suppose we have a data set containing three variables - X, Y and Z. They all have missing values. We wish to compute sum of all the variables.
data mydata2; set mydata; a=sum(x,y,z); p=x+y+z; run;The output is shown in the image below :
 |
| SAS : SUM Function vs Plus Operator |
In the output, value of p is missing for 4th, 5th and 6th observations.
14. How to identify and remove unique and duplicate values?
1. Use PROC SORT with NODUPKEY and NODUP Options.
2. Use First. and Last. Variables - Detailed Explanation
The detailed explanation is shown below :
SAMPLE DATA SET| ID | Name | Score |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | David | 45 |
| 1 | David | 74 |
| 2 | Sam | 45 |
| 2 | Ram | 54 |
| 3 | Bane | 87 |
| 3 | Mary | 92 |
| 3 | Bane | 87 |
| 4 | Dane | 23 |
| 5 | Jenny | 87 |
| 5 | Ken | 87 |
| 6 | Simran | 63 |
| 8 | Priya | 72 |
Create this data set in SAS
data readin; input ID Name $ Score; cards; 1 David 45 1 David 74 2 Sam 45 2 Ram 54 3 Bane 87 3 Mary 92 3 Bane 87 4 Dane 23 5 Jenny 87 5 Ken 87 6 Simran 63 8 Priya 72; run;
There are several ways to identify and remove unique and duplicate values:
PROC SORTIn PROC SORT, there are two options by which we can remove duplicates.
1. NODUPKEY Option 2. NODUP Option
The NODUPKEY option removes duplicate observations where value of a variable listed in BY statement is repeated while NODUP option removes duplicate observations where values in all the variables are repeated (identical observations).
PROC SORT DATA=readin NODUPKEY; BY ID; RUN;
PROC SORT DATA=readin NODUP; BY ID; RUN;
The output is shown below :
 |
| SAS : NODUPKEY vs NODUP |
The NODUPKEY has deleted 5 observations with duplicate values whereas NODUP has not deleted any observations.
Q. Why no value has been deleted when NODUP option is used?
Answer : Although ID 3 has two identical records (See observation 5 and 7), NODUP option has not removed them. It is because they are not next to one another in the dataset and SAS only looks at one record back.
To fix this issue, sort on all the variables in the dataset READIN.
To sort by all the variables without having to list them all in the program, you can use the keywork ‘_ALL_’in the BY statement (see below).
PROC SORT DATA=readin NODUP; BY _all_; RUN;The output is shown below :
 |
| SAS NODUP Output |
PROC SORT - Detailed Explanation
15. Difference between NODUP and NODUPKEY Options?
The NODUPKEY option removes duplicate observations where value of a variable listed in BY statement is repeated while NODUP option removes duplicate observations where values in all the variables are repeated (identical observations).
See the detailed explanation for this question above (Q14).16. What are _numeric_ and _character_ and what do they do?
1. _NUMERIC_ specifies all numeric variables that are already defined in the current DATA step.
2. _CHARACTER_ specifies all character variables that are currently defined in the current DATA step.
3. _ALL_ specifies all variables that are currently defined in the current DATA step.
Example : To include all the numeric variables in PROC MEANS.
proc means; var _numeric_; run;
Tutorial : Specify a list of variables
17. How to sort in descending order?
Use DESCENDING keyword in PROC SORT code. The example below shows the use of the descending keyword.
PROC SORT DATA=auto; BY DESCENDING engine ; RUN ;
18. Under what circumstances would you code a SELECT construct instead of IF statements?
When you have a long series of mutually exclusive conditions and the comparison is numeric, using a SELECT group is slightly more efficient than using IF-THEN or IF-THEN-ELSE statements because CPU time is reduced.
The syntax for SELECT WHEN is as follows :
SELECT (condition); WHEN (1) x=x; WHEN (2) x=x*2; OTHERWISE x=x-1; END;
Example :
SELECT (str);
WHEN ('Sun') wage=wage*1.5;
WHEN ('Sat') wage=wage*1.3;
OTHERWISE DO;
wage=wage+1;
bonus=0;
END;
END;
19. How to convert a numeric variable to a character variable?
You must create a differently-named variable using the PUT function.
The example below shows the use of the PUT function.
charvar=put(numvar, 7.) ;
20. How to convert a character variable to a numeric variable?
You must create a differently-named variable using theINPUTfunction.
The example below shows the use of the INPUT function.
numvar=input(charvar,4.0);
21. What's the difference between VAR A1 - A3 and VAR A1 -- A3?
Single Dash : It is used to specify consecutively numbered variables. A1-A3 implies A1, A2 and A3.
Double Dash : It is used to specify variables based on the order of the variables as they appear in the file,regardless of the name of the variable. A1--A3 implies all the variables from A1 to A3 in the order they appear in the data set.
Example : The order of variables in a data set : ID Name A1 A2 C1 A3
So using A1-A3 would return A1 A2 A3. A1--A3 would return A1 A2 C1 A3.
22. Difference between PROC MEANS and PROC SUMMARY?
1. Proc MEANS by default produces printed output in the OUTPUT window whereas Proc SUMMARY does not. Inclusion of the PRINT option on the Proc SUMMARY statement will output results to the output window.
2. Omitting the var statement in PROC MEANS analyses all the numeric variable whereas Omitting the variable statement in PROC SUMMARY produces a simple count of observation.
How to produce output in the OUTPUT window using PROC SUMMARY?
Use PRINT option.
proc summary data=retail print; class services; var investment; run;
23. Can PROC MEANS analyze ONLY the character variables?
No, Proc Means requires at least one numeric variable.
24. How SUBSTR function works?
The SUBSTR function is used to extract substring from a character variable.
The SUBSTR function has three arguments:
SUBSTR ( character variable, starting point to begin reading the variable, number of characters to read from the starting point)
There are two basic applications of the SUBSTR function:
RIGHT SIDE APPLICATIONdata _null_; phone='(312) 555-1212'; area_cd=substr(phone, 2, 3); put area_cd=; run;
Result : In the log window, it writes area_cd=312 .
LEFT SIDE APPLICATIONIt is used to change just a few characters of a variable.
data _null_ ; phone='(312) 555-1212' ; substr(phone, 2, 3)='773' ; put phone=; run ;
Result : The variable PHONE has been changed from(312) 555-1212 to (773) 555-1212.
Explanation : Other Character Functions25. Difference between CEIL and FLOOR functions?
The ceil function returns the smallest integer greater than/equal to the argument whereas the floor returns the greatest integer less than/equal to the argument.
For example : ceil(4.4) returns 5 whereas floor(4.4) returns 4.
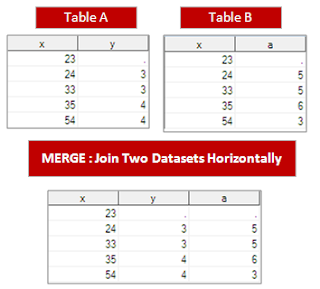
26. Difference between SET and MERGE?
SET concatenates the data sets where as MERGE matches the observations of the data sets.
SET
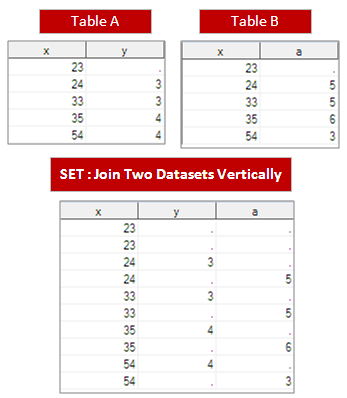
MERGE
Detailed Explanation : Data Step Merging
Detailed Explanation : Combine Data Sets
27. How to do Matched Merge and output only consisting of observations from both files?
Use IN=variable in MERGE statements. It is used for matched merge to track and select which observations in the data set from the merge statement will go to a new data set.
data readin; merge file1(in=infile1) file2(in=infile2); by id; if infile1=infile2; run;
28. How to do Matched Merge and output consisting of observations in file1 but not in file2, or in file2 but not in file1?
data readin; merge file1(in=infile1)file2(in=infile2); by id; if infile1 ne infile2; run;
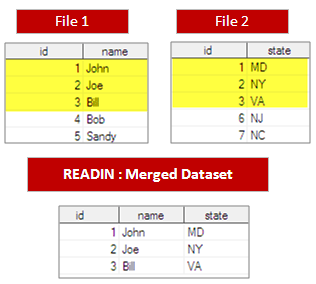
29. How to do Matched Merge and output consisting of observations from only file1?
data readin; merge file1(in=infile1)file2(in=infile2); by id; if infile1; run;
30. How do I create a data set with observations=100, mean 0 and standard deviation 1?
data readin;
do i=1 to 100;
temp=0 + rannor(1) * 1;
output;
end;
run;
proc means data=readin mean stddev;
var temp;
run;
31. How to label values and use it in PROC FREQ?
Use PROC FORMAT to set up a format.
proc format; value score 0 - 100=‘100-‘ 101 - 200=‘101+’ other=‘others’ ; proc freq data=readin; tables outdata; format outdatascore. ; run;
Tutorial : PROC FREQ Detailed Explanation
32. How to use arrays to recode set of variables?
Recode the set of questions: Q1,Q2,Q3...Q20 in the same way: if the variable has a value of 6 recode it to SAS missing.
data readin; set outdata; array Q(20) Q1-Q20; do i=1 to 20; if Q(i)=6 then Q(i)=.; end; run;
SAS Arrays and Do Loops Made Easy
33. How to use arrays to recode all the numeric variables?
Use _numeric_ and dim functions in array.
data readin; set outdata; array Q(*) _numeric_; do i=1 to dim(Q); if Q(i)=6 then Q(i)=.; end; run;
Note : DIM returns a total count of the number of elements in array dimension Q.
34. How to calculate mean for a variable by group?
Suppose Q1 is a numeric variable and Age a grouping variable. You wish to compute mean for Q1 by Age.
PROC MEANS DATA=READIN; VAR Q1; CLASS AGE; RUN;
35. How to generate cross tabulation?
Use PROC FREQ code.
PROC FREQ DATA=auto; TABLES A*B ; RUN;
SAS will produce table of A by B.
36. How to generate detailed summary statistics?
Use PROC UNIVARIATE code.
PROC UNIVARIATE DATA=READIN; CLASS Age; VAR Q1; RUN;
Note : Q1 is a numeric variable and Age a grouping variable.
37. How to count missing values for numeric variables?
Use PROC MEANS with NMISS option.
Types of Missing Values in SAS38. How to count missing values for all variables?
proc format; value $missfmt ' '='Missing' other='Not Missing'; value missfmt .='Missing' other='Not Missing'; run;
proc freq data=one; format _CHAR_ $missfmt.; tables _CHAR_ / missing missprint nocum nopercent; format _NUMERIC_ missfmt.; tables _NUMERIC_ / missing missprint nocum nopercent; run;
39. Describe the ways in which you can create macro variables
There are 5 ways to create macro variables:
- %Let
- Iterative %DO statement
- Call Symput
- Proc SQl into clause
- Macro Parameters.
40. Use of CALL SYMPUT
CALL SYMPUT puts the value from a dataset into a macro variable.
proc means data=test;
var x;
output out=testmean mean=xbar;
run;
data _null_;
set testmean;
call symput("xbarmac",xbar);
run;
%put mean of x is &xbarmac;
41. What are SYMGET and SYMPUT?
SYMPUT puts the value from a dataset into a macro variable where as SYMGET gets the value from the macro variable to the dataset.
Tutorial - Difference between SYMGET and SYMPUT
42. Which date function advances a date, time or datetime value by a given interval?
The INTNX Function advances a date, time, or datetime value by a given interval, and returns a date, time, or datetime value. Example : INTNX(interval,start-from,number-of-increments,alignment).
Tutorial: SAS Date Functions43. How to count the number of intervals between two given SAS dates?
INTCK(interval,start-of-period,end-of-period) is an interval function that counts the number of intervals between two give SAS dates, Time and/or datetime.
Tutorial : INTCK Function Explained44. Difference between SCAN and SUBSTR?
SCAN extracts words within a value that is marked by delimiters. SUBSTR extracts a portion of the value by stating the specific location. It is best used when we know the exact position of the sub string to extract from a character value.
45. The following data step executes:
Data strings; Text1=“MICKEY MOUSE & DONALD DUCK”; Text=scan(text1,2,’&’); Run;
What will the value of the variable Text be?
* DONALD DUCK [(Leading blanks are displayed using an asterisk *]46. For what purpose would you use the RETAIN statement?
A RETAIN statement tells SAS not to set variables to missing when going from the current iteration of the DATA step to the next. Instead, SAS retains the values.
Tutorial : RETAIN Statement47. When grouping is in effect, can the WHERE clause be used in PROC SQL to subset data?
No. In order to subset data when grouping is in effect, the HAVING clause must be used. The variable specified in having clause must contain summary statistics.
PROC SQL Made Easy48. How to use IF THEN ELSE in PROC SQL?
PROC SQL; SELECT WEIGHT, CASE WHEN WEIGHT BETWEEN 0 AND 50 THEN ’LOW’ WHEN WEIGHT BETWEEN 51 AND 70 THEN ’MEDIUM’ WHEN WEIGHT BETWEEN 71 AND 100 THEN ’HIGH’ ELSE ’VERY HIGH’ END AS NEWWEIGHT FROM HEALTH; QUIT;
49. How to remove duplicates using PROC SQL?
Proc SQL noprint; Create Table mergedtbl as Select distinct * from readin ; Quit;
50. How to count unique values by a grouping variable?
You can use PROC SQL with COUNT(DISTINCT variable_name) to determine the number of unique values for a column.
51. How to merge two data sets using PROC SQL?
PROC SQL Merging52. Difference between %EVAL and %SYSEVALF
%EVAL cannot perform arithmetic calculations with operands that have the floating point values. It is when the %SYSEVALF function comes into picture.
%let last=%eval (4.5+3.2); %let last2=%sysevalf(4.5+3.2); %put &last2;
53. How to debug SAS Macros
There are some system options that can be used to debug SAS Macros: MPRINT, MLOGIC, SYMBOLGEN.
Detailed Tutorial : SAS Macros Made Easy54.
%let x=temp; %let n=3; %let x3=result; %let temp3=result2;
Difference between &x&n , &&x&n , &&&x&n?
Solution : Multiple Ampersand Macro Variables
55. How to save log in an external file
Use PROC PRINTTO
proc printto log="C:\Users\Deepanshu\Downloads\LOG2.txt" new; run;
56. How Data Step Merge and PROC SQL handle many-to-many relationship?
Data Step MERGE does not create a cartesian product incase of a many-to-many relationship. Whereas, Proc SQL produces a cartesian product.
SAS : Many-to-Many Merge57. What is the use of 'BY statement' in Data Step Merge?
Without 'BY' statement, Data Step Merge performs merging without matching. In other words, the records are combined based on their relative position in the data set. The second data set gets placed to the "right" of the first data set (no matching based on the unique identifier - if data is not sorted based on unique identifier, wrong records can be merged).
When you use 'BY' statement, it matches observations according to the values of the BY variables that you specify.
58. Use of Multiple SET Statments
SAS : Use of Multiple SET Statements59. How to combine tables vertically with PROC SQL
PROC SQL : Combine tables vertically60. Two ways to reverse order of data
Reverse order of data61. Which is more faster- Data Step / Proc SQL
The SQL procedure performed better with the smaller datasets (less than approx. 100 MB) whereas the data step performed better with the larger ones (more than approx. 100 MB). It is because the DATA step handles each record sequentially so it never uses a lot of memory, however, it takes time to process one at a time. So with a smaller dataset, the DATA step is going to take more time sending each record through.
With the SQL procedure, everything is loaded up into memory at once. By doing this, the SQL procedure can process small datasets rather quickly since everything is available in memory. Conversely, when you move to larger datasets, your memory can get bogged down which then leads to the SQL procedure being a little bit slower compared to the DATA step which will never take up too much memory space.
If you need to connect directly to a database and pull tables from there, then use PROC SQL.
62. What does tranwrd function do?
The TRANWRD function is a string function that is used to replace occurrences of a specific word or phrase within a character string with a new word or phrase. It stands for "translate and replace word.
63. Explain PROC REPORT
PROC REPORT is a powerful SAS procedure used for creating customized tabular reports. It provides extensive options for formatting and arranging data in tables.


Thanks a lot for the wonderful questions and most of the people do mistake in this basic concept.This site is very useful and I have subscribed this channel and I am very excited whenever I will see the updates from your site. I will read all things which you have posted. Please help us to learn more on advanced SAS concepts.
ReplyDeleteAgaint thanks in advance and please continue the same.
Thank you for your appreciation.
DeleteThank you so much.Its really helpful for me.
ReplyDeleteThank you for your feedback. Glad you found it useful.
Deletexlent
ReplyDeleteif u know the MACROS plzz..show with these type view .its must helpful for us
ReplyDeleteSure. I will add some questions on SAS macros.
DeleteCheck out this link - SAS Macros Made Easy
Deletecan u upload sas interview questions on banking domain
Deleteit was very helpful thank you. little more on macro and proc sql will be really helpful.
ReplyDeleteSure. I will add some questions on macro and proc sql. Thank you for your feedback.
DeleteCheck out this link - SAS Macro Programming Made Easy
DeleteThanks Man.. It really helpe..
ReplyDeletehelped*
ReplyDeleteThis is awesome. I am preparing for an interview and could not have used a more well written and comprehensive article
ReplyDeleteThank you. All the best for your interview.
DeleteHi akriti.. Have u gave interview already if so please keep us updated on the interview Q's..
DeleteThanks
thanks a lot for such useful block of examples and concepts... it made me some what more clarified regarding the topics i was planning to be through.
ReplyDeletethanks again. great job
Thank you for your appreciation!
DeleteDoubt in que 3. MIssover vs Truncover...
ReplyDeletedata test_data;
infile datalines missover;
input age_ 4.;
datalines;
1
22
333
4444
;
run;
proc print data=test_data;
run;
The output is printing all values in missover option and not missing values, opposite of what that was mentioned on your site.
Use external file rather than data lines to read data into sas and you will get your answer.
Deletedata test_data;
infile "C:\Users\Deepanshu Bhalla\Desktop\test.txt" missover;
input age_ 4.;
run;
proc print data=test_data;
run;
Thanks.it really help
DeleteFirst of all i would like to thanku for providing such a precise and crisp basic questions to be taken care before heading to an interview. But i guess example of Nodup was wrong and there is no use _all_ keyword .
ReplyDeleteThank you for your feedback. I would request you to try NODUP example in SAS.
DeleteYes, i checked and giving the same output.
DeleteI have one more question. suppose we have a variable of character datatype(containing numeric data also) and we need to create two vble in such a way that numeric data and character data will come in differentiated.
CAN someone pls help.
You can use compress function to extract text and numbers from alphanumeric string. Check out this link - http://www.listendata.com/2015/04/sas-extracting-numbers-and-text-from.html
DeleteI am learning base SAS and i find this website very easy to follow and its really helpful, i just signed up for subscription today, and looking forward to learn new updates related to sas. i am going to give test for sas certification if you can post more certification practice question it will be very helpful. thanks a lot.
ReplyDeleteGlad you found it helpful. Sure, i will post more certification practice questions. Thanks!
DeleteGreat work man. Definitely awsome data for those , preparing for there intrrviews.
ReplyDeleteThanks man for this great work. And keep posting like this great information.
Thank you for your appreciation!
Deletethanks a lot Deepanshu. this one is a very good collection of Q&A. could you please post Q&A of Proc SQL and macros.
ReplyDeleteCheck out this link - SAS Macro Programming Made Easy
DeleteHey .. Great Job! Just cracked an interview because of this post.
ReplyDeleteCongratulations! Glad to know that :-)
DeleteCan u give us more info about the interview and Questions that were asked?? @ Anonymous
DeleteThanks. Answers werereally h elpfull. good job.
ReplyDeletewhich infile option use for read given data.
ReplyDeleteVVVVV 3 2 3 4
VAR 2 3
SSSSS 3 2
Thnks ..Great Job ..can you please add more questions ?
ReplyDeletevery useful compilation thanks a lot
ReplyDeleteTHANK YOU VERY MUCH FOR YOUR MARVELOUS WORK ,WHICH IS VERY HELP FULL, AND I REQUEST YOU POST MACROS MATERIALS
ReplyDeleteThis is very helpful...great work! Thank you :)
ReplyDeleteVery helpful and great work. Can you please post the differences between proc means, proc summary and proc univariate.
ReplyDeleteIam pushpa.I did my MSC statistics .iam learning SAS. Which project should I take either banking n finance or clinical trails .which one should really helpful to my career in analytical side
ReplyDeleteI would say "Banking & Finance" project as jobs in BFSI industry are more than the pharma industry, Thanks!
DeleteGood going Deepanshu... Found it really healpful...
ReplyDeleteDeepanshu, I need a analytics +sas resume for fresher, I hope you will help me.
ReplyDeleteGood set of questions.. very helpful.. keep writing..
ReplyDeletethanks for a wonderful questions keeps going on but i need more questions on macros will u please
ReplyDeletegreat job.present scanario which sector to use sas. and who r looking for job in sas, r they have any oputunite on sas domain in future... is it better course for learning?
ReplyDeletevery well done Deepanshu. There is no website like yours with such good interview questions and answers. keep going!
ReplyDeleteNice Questions and Very Well Presented. Thank You!!!
ReplyDeleteGreat article. Can you include some info on new things in SAS 9.4 version as most interviewer ask this kind of questions and there are lot more addition to the normal function in SAS 9.4. It would be great if look into this topics.
ReplyDeleteNice questions and answers.Very much helpful.Thank You!!!!!
ReplyDeleteThe Explanation for basic SAS is very useful. Can you do same thing for Macro and Array?
ReplyDeleteCheck out this link - SAS Macro Programming Made Easy
DeleteHello.
ReplyDeleteThere is a mistake at question 28.
The question was: "How to do Matched Merge and output consisting of observations in file1 but not in file2?"
The answer in this article is wrong.
The answer would be:
data readin;
merge file1(in=infile1) file2(in=infile2);
by id;
if infile1 = 1 and infile2 = 0;
run;
Your 'if' (infile1 ne infile2) outputs cases when infile1 = 1 and infile2= 0 but also cases when infile1 = 0 and infile2 = 1: i.e. respectively observations in file1 but not in file2 and observations in file2 but not in file1.
My 'if' (infile1 = 1 and infile2 = 0) represents only cases when infile1 = 1 and infile2= 0: i.e. observations in file1 but not in file2.
Regards.
Cédric Guilmin
I have rephrased the question to make it more clear. Thanks for writing to me.
DeleteNo problem ;-)
DeleteDeepanshu keep it up nice job this artical cleared my almost all questions thank u.
ReplyDeleteGlad you found it helpful.Cheers!
DeleteDm statement ia used to clean the windows like editor,output and log and we can export the log. Let me explain is there any specific meaning for dm r any fullform for dm.
ReplyDeleteDM stands for Display Manager.
DeleteWe have proc datasets it is performing append,copy,delete,modify.Though it is performing all these why we are using still all these proc procedures separately like proc copy,proc delete,proc append.Is there any limitation to proc datasets
ReplyDeletePROC DELETE is faster than PROC DATASETS when you want to remove a few data sets from the library. On the other hand, if you need to delete an entire library, then PROC DATASETS is the best tool. Read about "how PROC Datasets keeps an in-memory directory"
DeleteHi Deepanshu,
ReplyDeleteMe planning to give the base sas certification exam by 15th Jan, Please provide me some dummy questions to clear the exam...
Check out this link - SAS Base Certification Questions and Answers
Deletehello sir,
DeleteI am already pursuing a course on SAS.I wanted to know is the pnline certification course required for a job?
Which online certification you are referring to? Is it base SAS certification course?Certification does not help much. At the end, you have to crack interview. What matters is your knowledge about practical application of SAS Programming. In short, It's good to be Base or Advanced SAS certified but it would not guarantee you a job.
DeletePlz help me on this :
ReplyDeleteId age salary
1 23 3000
2 34 5000
4 26 2000
4 26 2000
5 32 5000
5 32 4000
Output:
Id age salary
1 23 3000
2 34 5000
4 26 4000
5 32 9000
Kindly tell me how to achieve this. Thanks in advance. Plz help
using NODUPKEY BY ID WILL do the trick
Deletedata temp;
Deleteinput Id age salary;
cards;
1 23 3000
2 34 5000
4 26 2000
4 26 2000
5 32 5000
5 32 4000
;
run;
proc sql;
select distinct ID, Age, sum(salary) as salary
from temp
group by ID;
quit;
Thanks a lot brother. Sas seems to be getting easier and a lot easier courtsey You and this wonderful website listen data. Amazing job.
DeleteCongrats
MAC
proc sort data=dsn nodupkey;
Deleteby id;
run;
You can use below code for that..
DeleteProc sort data = temp;
By id;
Run;
Data temp1(rename=(salary1=salary));
Set temp;
By id;
If first.id then salary1=salary;
Else salary1+salary;
If last.id then output;
Drop salary;
Run;
Thankq so much..Its really helpful for me.great job..
ReplyDeleteamazing , yaar you know everything
ReplyDeleteHow to reverse a set of numbers without sorting..
ReplyDeleteFor example, 2 9 6 4 3 8
This was an interview question as well :)
Nice question! Check out the solution -
Deletedata temp;
input var1 @@;
cards;
2 9 6 4 3 8
;
run;
data temp2;
do i = nobs to 1 by -1;
set temp nobs = nobs point=i;
output;
end;
stop;
run;
Thank you Deepanshu Bhalla :)
ReplyDeleteHello sir,
ReplyDeleteyour post has been very helpful .I am already learning sas.I have also done my M.A. in economics with specialization in Econometrics.will this be of any added advantage sir?
Some companies give preference to economics or statistics graduates for predictive modeling profiles. FYI - I am also an economics graduate.
DeleteHi deepanshu....
ReplyDeleteyour content is amazing...really helpful...could u help me with this query..if a datavalue is missing in the middle of the record what infile option is to be used...i used both missover and truncover options..both resulted in the same way... i did not get the desired output...
The following is my example:
LANGKAMM SARAH E0045 Mechanic
TORRES JAN E0029 Pilot
SMITH MICHAEL E0065
LEISTNER COLIN Mechanic
TOMAS HARALD
WADE KIRSTEN E0126 Pilot
WAUGH TIM E0204 Pilot
Deletedata employee;
input Name & $15. id $5. profession $10.;
infile datalines missover;
datalines;
LANGKAMM SARAH E0045 Mechanic
TORRES JAN E0029 Pilot
SMITH MICHAEL E0065
LEISTNER COLIN Mechanic
TOMAS HARALD
WADE KIRSTEN E0126 Pilot
WAUGH TIM E0204 Pilot
run;
Hi, Neelima is the above code is ok for your query??
its good information.....
ReplyDeleteAppreciate the work Deepanshu. It really is a crisp collection with the appropriate links for the detail.
ReplyDeleteThank you for your appreciation!
DeleteDeepanshu, I do not have words to appreciate you. The Questionnaire you have created is a 'One-Stop-Shop' for all the SAS lovers & Users. Please continue to add on the good work. Wish you all the Best!. Regards, Rakesh
ReplyDeleteThank you for your kind words. I am glad you found it helpful. Cheers!
DeleteNice!! Good interview questions and answers for base SAS. Thanks
ReplyDeleteThank you for your appreciation!
DeleteReally helps in understanding the concepts more clearly.
ReplyDeleteSuch a nice collection of interview questions and answers. The best thing is that your site looks so user friendly and one feels like reading a book instead of webpage. Great work !!!
ReplyDeleteThank you for stopping by my blog!
Deletethank q sir ur explantion is good it is really helpfull to me
ReplyDeleteGlad you found it helpful. Cheers!
DeleteDear Sir
DeleteHow to find cumulative sum of a variable.please help me
TIA
data abcd;
Deleteinput x y;
cards;
1 25
1 28
1 27
2 23
2 35
2 34
3 25
3 29
;
run;
data aaa;
set abcd;
retain z 0;
z = z + y;
run;
Deletehi sr,
I have a real time scenario
I have a dataset with the following info
emp_id currency$
1234 USD
1289 USD
1389 INR
1456 INR,USD
1567 USD,GBP,INR
I need ouput like this
e_id currency$
1234 USD
1234 USD
1289 USD
1389 INR
1456 INR
1456 USD
1567 USD
1567 GBP
1567 INR
1567 INR
how to do it,please help me
Hi,
DeleteThis is Satish.
Please find the below solution.
data EMP_CURR;
input emp_id currency$20.;
CUUR_COUNT_DEL=LENGTH(currency)-length(compress(currency,","));
call symput('x_c',max(CUUR_COUNT_DEL)+1);
cards;
1234 USD
1289 USD
1389 INR
1456 INR,USD
1567 USD,GBP,INR
1897 USD,INR,AFN,DZD,ABC
;
%put &x_c;
data EMP_CURR_1 (drop=i currency);
set EMP_CURR;
array scan_(&x_c.) $;
do i= 1 to &x_c.;
scan_(i)=scan(currency,i,",");
end;
run;
data EMP_CURR_2(keep=emp_id currency);
set EMP_CURR_1;
array scan_(&x_c.) $;
do i= 1 to &x_c.;
if scan_(i) ne " " then currency=scan_(i);
output;
end;
run;
proc sort data=EMP_CURR_2 nodup;by emp_id;
run;
Do you have any content and interview questions and answers on SAS Graphs please post them.
ReplyDeleteThank you in advance.
Nice!! Good interview questions and answers for base SAS. Thanks
ReplyDeleteThank you for stopping by my blog!
DeleteAwsome!!! Really helpful...pls also try to post some scenario based questions as well..that would be really great.Looking forward to it!
ReplyDeletethis was excellent stuff to go through thanks for uploading and can u upload prog 3 questions if possible
ReplyDeletecan anyone suggest the best institue in delhi for sas and will it be beneficial for B.Sc maths background student
ReplyDeleteNice.... really very helpfull.add more questions on base sas.and please add few questions from domain too on sdtm and AdaM
ReplyDeleteI am working in sql server and .net but want to move in SAS is it a good idea?
ReplyDeleteI am Post Graduate in Statistics.I keep on following this site. I learned SAS.But as of my knowledge openings for freshers are low.I dont have working knowledge on SAS.I want to learn Advanced excel and statistical topics under excel.With excel also I have the chance to become a data analyst.I thought after that move on to SAS is easy. Is my thinking is right? If it good, what are topics that i have to learn? Can u please answer me?
ReplyDeleteUnless you excel in VBA after you complete your session with EXCEL, I would recommend you start with SAS directly. There is less necessity to take a detour.
Deletereally helpful as language is quite simple.
ReplyDeleteThis list of Q&A is really comprehensive! I spent a day and currently stopped Q26, and will continue to finish the rest tomorrow. I have watched SAS official tutorials but none of those are as helpful as the questions in this blog. I would recommend newbies, like myself, spend extra time to expand a little bit beside the scope of each question, and don't just look for answers for questions, instead treat each question seriously and key in the codes in SAS to see how the answer works. By practicing along the way, I have developed a pretty good sense of the data structure and common syntaxes. Good luck everyone!
ReplyDeleteHappy Studying SAS Enthusiast!
DeleteThanks a lot for the q&a.
ReplyDeleteIf any opening related to this profile please please contact me I realy need one job 8745991176
ReplyDeleteReally this is very helpful site. Could be more helpful if scenario base questions are included. Thank you very much.
ReplyDeleteThank you for all the questions. It helps alot
ReplyDeletegood going buddy,, found it very helpful...
ReplyDeletekeep posting
Thanx a ton
Thanks for this material.Really Help full alot.
ReplyDeleteThis is so much helpful and easy to understand. Till now, my every query got answered through these blogs.
ReplyDeleteThanks a lot :)
hi,
ReplyDeleteI wanted to learn tableau but don't see it on your blog. Any plans to add it
good stuff,and it is very useful for freshers as well as experienced candidates....'thank you sir'....
ReplyDeleteHey...Nice blog...great for interview preparation ..Thanks
ReplyDelete
Deletehi sr,
I have a real time scenario
I have a dataset with the following info
emp_id currency$
1234 USD
1289 USD
1389 INR
1456 INR,USD
1567 USD,GBP,INR
I need ouput like this
e_id currency$
1234 USD
1234 USD
1289 USD
1389 INR
1456 INR
1456 USD
1567 USD
1567 GBP
1567 INR
1567 INR
how to do it,please help me
Hi,
ReplyDeleteThis is satish.
Please find the solution.
data EMP_CURR;
input emp_id currency$20.;
CUUR_COUNT_DEL=LENGTH(currency)-length(compress(currency,","));
call symput('x_c',max(CUUR_COUNT_DEL)+1);
cards;
1234 USD
1289 USD
1389 INR
1456 INR,USD
1567 USD,GBP,INR
1897 USD,INR,AFN,DZD,ABC
;
%put &x_c;
data EMP_CURR_1 (drop=i currency);
set EMP_CURR;
array scan_(&x_c.) $;
do i= 1 to &x_c.;
scan_(i)=scan(currency,i,",");
end;
run;
data EMP_CURR_2(keep=emp_id currency);
set EMP_CURR_1;
array scan_(&x_c.) $;
do i= 1 to &x_c.;
if scan_(i) ne " " then currency=scan_(i);
output;
end;
run;
proc sort data=EMP_CURR_2 nodup;by emp_id;
run;
Awesome solution it's great to learn..
DeleteThanks Satish
Really Nice and very helpful SAS QnA
ReplyDeleteDo you have simillar in SAS VA ?
ReplyDeleteHi everyone,
ReplyDeleteI have a table/dataset as below:
Name Skill
Amit Informatica
Amit SQL
Ram Abinitio
Bhim SAS
Bhim SQL
And I need output using SAS as:
Name Abinitio. Informatica SAS SQL
Amit No Yes No Yes
Bhim No No Yes Yes
Ram Yes No No No
Could you please help me with the code?
data temp;
Deleteinput name $ Skill $12.;
cards;
Amit Informatica
Amit SQL
Ram Abinitio
Bhim SAS
Bhim SQL
;
run;
proc transpose data=temp out=temp2 (drop=_NAME_);
by name notsorted;
id Skill;
run;
proc format;
value flag
.='No'
1='Yes';
run;
data temp22;
set temp2;
format SAS SQL Informatica Abinitio flag.;
run;
Thank you Deepanshu
DeleteHi, above is not working correct as it gives error as numeric format for character formating there is slight change in code,
Deletedata temp;
input name $ Skill $12.;
cards;
Amit Informatica
Amit SQL
Ram Abinitio
Bhim SAS
Bhim SQL
;
run;
proc transpose data=temp out=temp2 (drop=_NAME_);
by name notsorted;
id Skill;
var name;
run;
proc format;
value $ flags
" "='No'
other='Yes';
run;
data temp22;
set temp2;
format SAS SQL Informatica Abinitio flags.;
run;
thak you soo much.
ReplyDeletequestion no. 28 answer is wrong, plz verify
ReplyDeleteHi,
ReplyDeleteReferring to Q. 10(Point number 2):
"WHERE can be used as a data set option while IF cannot be used as a data set option"
I believe there is a Typo for using "cannot" rather than using "can".
Thanks
Helpful....
ReplyDeleteHi,
ReplyDeleteI have a dataset with n number of columns .my qn is I am searching one word ,I want to print only that column names wherever that word exists in Columns.?
Please check vname function with array referenced on the variables/columns you want the condition on.
DeleteTx
ReplyDeleteHi
ReplyDeleteCould you breif explanation of proc means it means what is N,mean,median like that
Hi,How can i remove selected observations and when i can use more set variable in data step if i have two data set?
ReplyDeletePlease add some more questions that are being asked on SAS interviews.
ReplyDeletethank you so much yar it is useful for us
ReplyDeleteit is very use full to me thanks a lot
ReplyDeletethank you
ReplyDelete